- Home
- Blog
- Plastic Polymer Composite Article
- What Is Injection Molding? Applications, Processes, and Key Products Explained!
What Is Injection Molding? Applications, Processes, and Key Products Explained!
Injection molding is a core technology in the manufacturing industry, widely used in the production of plastics and composite materials. This process is characterized by its efficiency and precision, enabling the rapid mass production of complex-shaped products. This article introduces the basic concepts of injection molding and dives deep into its process flow, mold structure, and major applications.
〈Extended Reading:What is Extrusion? Principles, Applications, and Its Benefits for Long Plastic Products〉
What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to create components from thermoplastic or thermosetting plastics. In this process, plastic granules are heated in the barrel of an injection molding machine until they reach a molten state. The molten plastic is rapidly forced under pressure by a screw or plunger through the nozzle and into a closed mold. As the plastic cools and solidifies within the mold, the mold is opened, and the finished product is removed.
Applications and Industries of Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding enables the production of a wide range of products, including automotive parts, electronic components, medical devices, household goods, and baby toys. The materials and applications of injection molding are highly versatile, allowing for the creation of precise, complex, and diverse products through injection molds. This versatility has made injection molding an indispensable technology in the manufacturing industry. Below are its main application areas:
- Automotive Industry: Injection molding machines play an indispensable role in the production of various automotive parts and interior components, significantly improving production efficiency while ensuring superior product quality.
- Electronics Industry: Injection molding technology is widely used in the manufacturing of enclosures and connectors for electronic products. It ensures products are both aesthetically refined and meet strict engineering design standards.
- Medical Devices: Injection molding technology excels in manufacturing high-precision medical devices and instruments that meet strict specifications, ensuring their safety and reliability.
- Packaging Industry: Injection molding technology is widely used in the production of plastic containers, covering areas such as food and cosmetic packaging. It is an important process in the packaging industry.
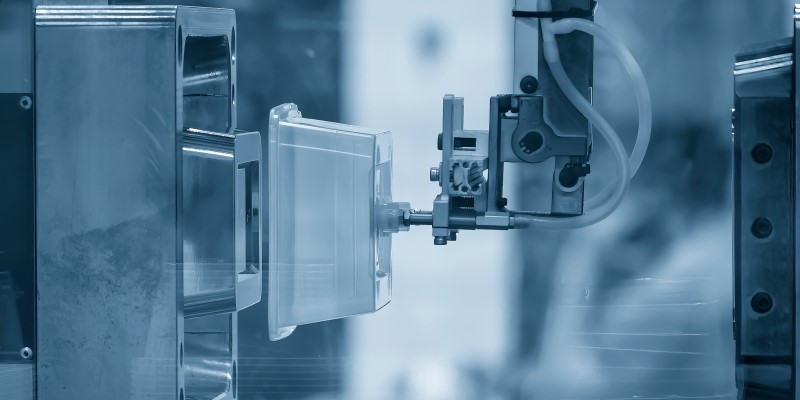
Internal Structure and Key Components of Injection Molding Molds Dies
The primary role of injection molding dies is to shape plastics into specific forms during the molding process while also enhancing their strength and performance. Molds perform tasks that cannot be achieved by molding equipment alone, transforming raw plastics into practical shapes or functional products. Injection molding molds dies are designed with varying structures depending on product design, molding equipment, and material properties; however, their basic design shares a largely uniform framework. The most common types of molds are extrusion molds and injection molds. Below, we will explore the three main structures of injection molds.
Gating System
The gating system is a vital part of an injection molding mold die. It refers to the flow channel structure through which the molten plastic travels from the injection machine nozzle into the mold cavity. This system includes the sprue, runner, and gate. The primary function of the gating system is ensuring smooth flow of molten plastic into the mold cavity, including deep regions, resulting in plastic parts with clear external contours and excellent internal quality.
Molding Components
The molded components form the core of an injection molding die, shaping the final product. It includes the moving mold cavity, fixed mold cavity, core, and vent holes. The moving mold is installed on the moving platen of the injection molding machine, while the fixed mold is installed on the fixed platen. During the injection molding process, the moving mold and fixed mold close to form the injection system and mold cavity; when the mold opens, the moving mold and fixed mold separate, facilitating the removal of the molded plastic product.
Structural Component
Structural components are the essential elements forming the mold's framework, including those responsible for guiding, ejection, core pulling, and parting functions. In injection molds, a guiding system is typically composed of four sets of guide pins and bushings. Additionally, internal and external tapered surfaces are sometimes incorporated into the moving and fixed molds to aid in precise alignment.
The 5 Major Processes of Injection Molding
The injection molding process can be divided into five main steps, commonly referred to as the injection molding cycle. The entire process, from injecting plastic into the mold to producing the final product, consists of the following stages:
- Clamping: The mold is closed, preparing for injection.
- Filling: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, with holding pressure applied to compensate for shrinkage during cooling.
- Holding/Measurement: The screw rotates to fill the plastic into the injection chamber. After filling is complete, the screw retracts to the rear position, preparing the required amount of plastic for the next injection.
- Cooling: The plastic product is fully cooled within the mold until it solidifies.
- Ejection: The mold opens, releasing the finished plastic product.
PVC Compound: A Key Product in Injection Molding
APEX's PVC Compound is extensively used in injection molding, primarily as an additive to improve the color and performance of plastic products. The compound is a blend of PVC resin, pigments, fillers, stabilizers, and other additives, available in granular form. PVC Compound for injection molding come in two types: rigid and flexible, to cater to different needs.
〈Extended Reading:A Comparative Study of PVC Compound and Masterbatch: Key Materials in Plastics Processing〉
〈Recommended Product: PVC Compound〉
Rigid Compounds for Injection Molding
Rigid PVC compounds boast excellent mechanical strength, temperature resistance, and impact resistance. It is widely used in various industrial applications, especially for products demanding high durability and precision.
Flexible Compounds for Injection Molding
Flexible PVC compounds are ideal for products demanding durability, elasticity, and enhanced flexibility. They are widely used in the production of footwear, transportation components, and daily-use products. These compounds deliver outstanding processing performance and versatile customizability.
Five Key Process Conditions in Injection Molding
Injection molding is a complex process requiring precise control of multiple parameters. Even minor variations in these parameters can significantly affect product quality. Below, we will detail the five key process conditions in injection molding: temperature, pressure, speed, time, and position.
1. Temperature
Key temperatures in injection molding include barrel, nozzle, and mold temperatures. The first two primarily affect the plastic's melting and flow, while mold temperature mainly influences the plastic's flowability and cooling rate.
2. Pressure
Injection pressure is the maximum pressure applied during mold filling. Initially, a lower injection pressure should be selected to ensure the plastic fills the mold smoothly and to prevent the formation of flash. This setup is typically considered the most optimal choice.
3. Speed
Injection speed includes screw rotation, filling, mold movement, and ejection speeds. The selection of injection speed is influenced by the design of the product and the material requirements. Below, we will explore how the speed of entry into the gate affects the final product:
- Slow injection speed: May cause short shots or wave-like "vinyl record" patterns on the product surface.
- Moderate injection speed: Results in a smooth, refined product surface, free from noticeable flow marks, shrinkage, or bubbles.
- Slightly fast injection speed: May lead to localized fogging or an orange-peel pattern near the gate.
- Excessively fast injection speed: May cause visible jetting marks on the product, leading to in noticeable defects.
4. Time
The injection cycle is the total time required to complete one thermoplastic injection molding process. Cooling time and injection time are critical parts of the cycle, determining the final product's performance and quality.
How Long Is the Injection Cycle Time?
Injection filling time for general products is relatively short, typically around 2 to 10 seconds, depending on the plastic material and the product's shape and size. For large or thick-walled products, the filling time can exceed 10 seconds.
The holding time for general products is usually between 20 to 100 seconds. However, for large or thick-walled products, it may be extended to 1 to 5 minutes or even longer. Cooling time is designed to ensure the product can be demolded without deformation while keeping it brief. It typically ranges from 30 to 120 seconds but can be extended for large or thick-walled products.
5. Position
Position settings in the injection molding process include feed , filling , and holding pressure transition points. For single-cavity molds, the molten plastic typically enters the cavity through the gate via the runner. For multi-cavity molds, a runner system is required to distribute the plastic evenly to each cavity.
conclusion
APEX offers customized injection molding solutions designed to meet customer requirements. Whether it's the size, shape, or performance requirements of rigid or flexible injection molding compounds, we can adjust specifications to accommodate various manufacturing demands. Additionally, APEX provides diverse transportation solutions, ensuring timely and direct delivery to your facility. Feel free to contact us anytime to learn more.
〈Extended Reading:What is Calcium Carbonate? A Comprehensive Guide to Its Production, Types, and Applications!〉
〈Extended Reading:What is Filler Masterbatch? Explanation of the Filler Masterbatch Process and the Applications of Calcium Carbonate Masterbatch〉
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- What is limestone powder? Applications of limestone powder
- What is filler masterbatch resin? How is it applied?
- Top 10 types of plastics used in injection molding technology
- What are fillers? Classification and applications of plastic fillers
- What are plastic additives? 11+ common types of plastic additives