- Home
- Blog
- Plastic Polymer Composite Article
- What is Extrusion? Principles, Applications, and Its Benefits for Long Plastic Products
What is Extrusion? Principles, Applications, and Its Benefits for Long Plastic Products

Do you need to produce large volumes of plastic tubing, films, or other elongated products? Extrusion molding is the solution! By precisely controlling temperature and pressure, molten plastic is formed into continuous shapes of varying profiles This article explores the principles of extrusion, advantages and drawbacks, the range of products it can create, and its applications across industries—offering inspiration for your product development.
What is Extrusion Molding?
Extrusion molding, also called extrusion molding, is a manufacturing process used to produce objects with a uniform cross-sectional shape. Material is forced through a custom-designed die, ensuring consistency in shape. This process can be continuous for producing extended materials or batch-based for creating segmented parts.
Understanding the Extrusion Molding Process
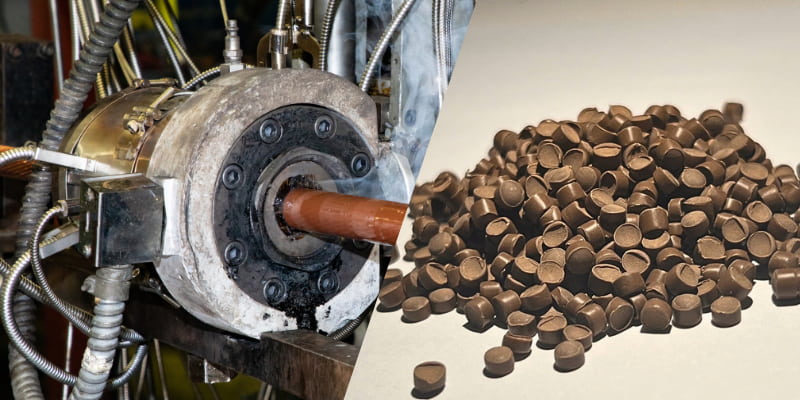
Extrusion molding is a widely used plastic manufacturing process for products like pipes, curtain tracks, straws, rods, and fibers. Polymer granules are melted, combined with additives, and pushed through a die to create a continuous profile. The steel die's shape determines the cross-sectional design, such as T-shaped, U-shaped, square, or circular. The extruded material is solidified through air or water cooling, then customized or cut to specific lengths.
The Pros and Cons of Extrusion Molding
Extrusion molding is a process in which liquid plastic is forced through a specific cross-section to form the desired shape. This process requires precise control of temperature and pressure to ensure the plastic maintains its shape as it exits the mold. In the following sections, we will delve into the advantages and challenges of extrusion molding, providing a comprehensive overview of this manufacturing technique.
The Advantages of Extrusion Molding
-
Supports Complex Shapes: Extrusion can produce intricate 2D profiles and effectively process brittle materials due to its controlled shear and pressure.
-
Cost-Effective for Long Products: Particularly suitable for producing continuous or elongated profiles, extrusion offers lower costs compared to injection molding.
- Wide Material Compatibility: Applicable to most thermoplastics, synthetic rubbers, and even metals or ceramics, making it versatile for construction, packaging, and other industries.
- Customizable Surface Finishes: Extruded materials often feature smooth surfaces and can develop specific textures through processing.
The Disadvantages of Extrusion Molding
- Shape Limitations: Primarily restricted to producing pipes, sheets, rods, and cables, offering limited design flexibility.
-
Dimensional Variability: Cross-sectional or dimensional changes require a new die, leading to increased production time and costs.
-
Environmental Challenges: High energy consumption during heating and cooling, coupled with limited durability of extruded products, raises sustainability concerns.
- Scaling Constraints: While initial tooling costs are lower, the cost-efficiency does not scale as effectively as injection molding.
Key Uses and Industries of Extrusion Molding
Extrusion molding is primarily used for manufacturing continuous, elongated materials with a consistent cross-sectional shape, such as profile pipes (custom-shaped pipes) and films. Extrusion molding can also be combined with blow molding to produce plastic bags and pouches or foam materials. This technique is widely applied in the plastics industry, with over 60% of global plastic products made using extrusion molding, making it especially ideal for fixed cross-section requiring continuous production. Extrusion molding finds broad applications across various industries, with common products including:
Construction Industry
Extrusion is ideally suited for manufacturing hollow pipes and tubing, including PVC water pipes and sewage pipes with diameters up to several feet. It is also extensively applied in producing PVC floor tiles, door and window frames, blinds, foam boards, wire conduits, folding doors, and more.
Packaging Industry
Extrusion molding can produce extremely thin sheets and films, which can be used as transparent alternatives to glass, as well as for plastic beverage bottles and pharmaceutical blister packaging. Other common uses include food wrap, shrink wrap, and heat-shrinkable films.
Electronics Industry
Common extrusion molding products include transparent IC packaging tubes, electrical components, wires, cables, and fiber optic lines. Another important application is insulation for wiring in electrical cables.
Medical Industry
The medical industry requires extremely small tubing for a variety of diagnostic and surgical applications. Extrusion molding technology can provide these tubes in different diameters while ensuring performance remains unaffected. Examples include products like breathing tubes, drainage tubes, feeding tubes, and IV bags.
Automotive Industry
Plastic extrusion molding is widely used in the automotive industry, including the production of tubing for engines and fuel lines, as well as components like trim panels, wiring, and seals.
Application Products in Extrusion Molding - PVC Compound
In the manufacturing and plastic processing industries, PVC compound is one of the most widely used plastic additives. APEX’s “PVC Compound” is a plastic blend specifically designed for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resin, widely applied in fields such as cables, building materials, and piping. This compound offers excellent molding performance, chemical stability, and weather resistance, providing a reliable performance foundation for products, making it an ideal choice for the plastics processing industry!
〈Extended Reading: A Comparative Study of PVC Compound and Masterbatch: Key Materials in Plastics Processing〉
〈Recommended Product: PVC Compound〉
Comparison of Extrusion Molding with Other Plastic Molding Methods
Extrusion molding is one of the most common methods in plastic processing, but it is not the only option. Different plastic products require different molding methods to achieve optimal quality and efficiency. Below, we will compare extrusion molding with other common plastic molding methods, such as injection molding and compression molding.
Comparison of Extrusion, Injection, and Compression Molding
| Extrusion Molding | Injection Molding | Compression Molding | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forming Principle | Thermoplastic material is heated and softened, then extruded into a mold to shape | Melted plastic is injected into stainless steel mold, then cooled to remove finished product | Plastic is compressed into mold cavity under high temperature and pressure until solidified |
| Product Shape | Elongated products with fixed cross-sections | Products with various complex shapes | Large and complex shaped products |
| Production Efficiency | High, suitable for long-term continuous production | High, suitable for mass production | Low, with longer production cycle |
| Equipment Cost | Low | High | Medium |
| Mold Cost | Low (simple mold) | High (expensive mold costs) | Medium (moderate mold-making cost) |
| Applicable Industries | Industries requiring large-scale production of continuous products | Widely applicable, steel molds can create complex and diverse products | Suitable for complex shapes, high impact resistance, high strength products |
Conclusion
APEX's PVC Compound is an excellent solution for extrusion molding! We carefully select high-quality PVC resins and offer highly customized formulations to meet the specific needs of various industries. Our compound's excellent coloring performance enhances the visual appeal of your products, while its versatile modification capabilities improve mechanical properties and weather resistance. Contact us to learn how to enhance the performance of your plastic products!
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- What is limestone powder? Applications of limestone powder
- What is filler masterbatch resin? How is it applied?
- Top 10 types of plastics used in injection molding technology
- What are fillers? Classification and applications of plastic fillers
- What are plastic additives? 11+ common types of plastic additives